The Parallel block is a container that executes multiple instances concurrently for faster workflow processing. Process items simultaneously instead of sequentially.
Parallel blocks are container nodes that execute their contents multiple times simultaneously, unlike loops which execute sequentially.
Configuration Options
Parallel Type
Choose between two types of parallel execution:
Count-based Parallel - Execute a fixed number of parallel instances:
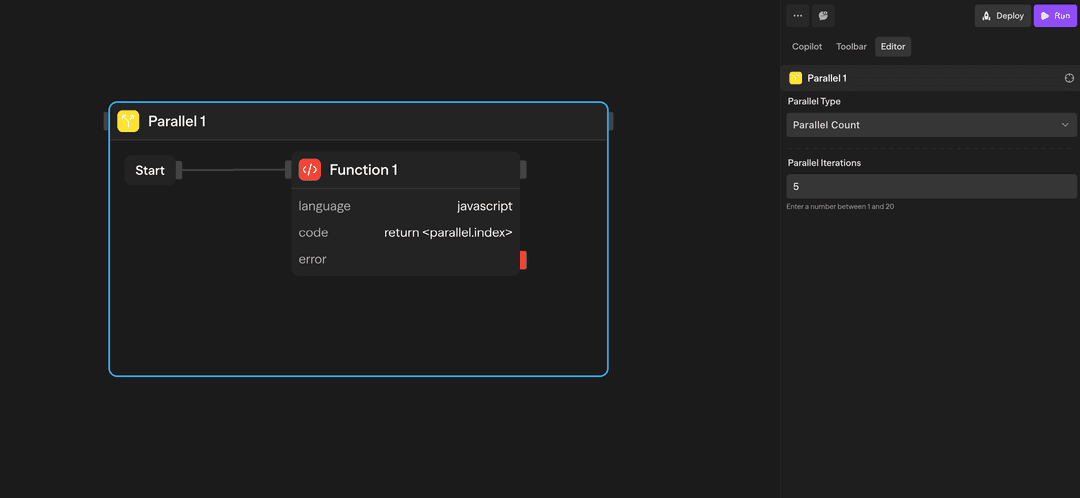
Use this when you need to run the same operation multiple times concurrently.
Example: Run 5 parallel instances
- Instance 1 ┐
- Instance 2 ├─ All execute simultaneously
- Instance 3 │
- Instance 4 │
- Instance 5 ┘Collection-based Parallel - Distribute a collection across parallel instances:
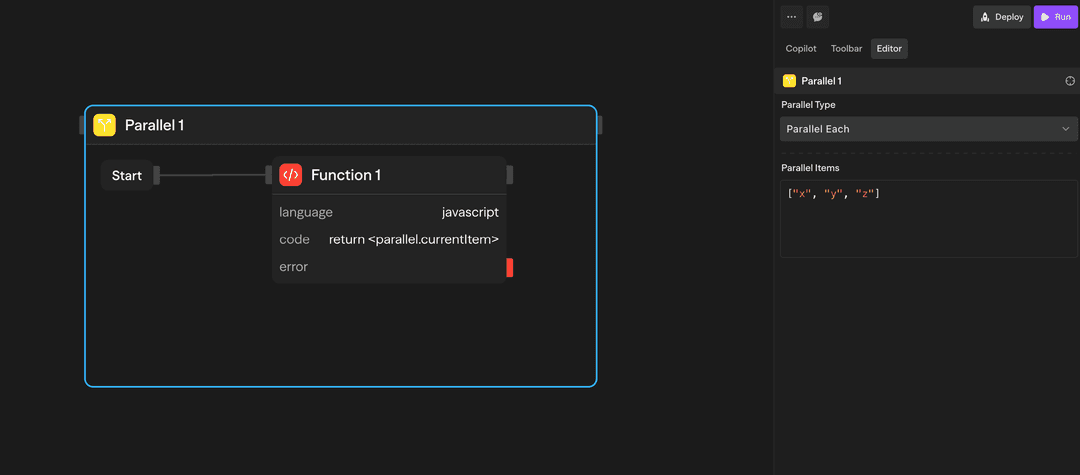
Each instance processes one item from the collection simultaneously.
Example: Process ["task1", "task2", "task3"] in parallel
- Instance 1: Process "task1" ┐
- Instance 2: Process "task2" ├─ All execute simultaneously
- Instance 3: Process "task3" ┘How to Use Parallel Blocks
Creating a Parallel Block
- Drag a Parallel block from the toolbar onto your canvas
- Configure the parallel type and parameters
- Drag a single block inside the parallel container
- Connect the block as needed
Referencing Parallel Data
There's an important distinction between referencing parallel data from inside vs outside the parallel block:
Inside the parallel, use <parallel.> references to access the current instance context:
<parallel.index>: Current instance number (0-based)<parallel.currentItem>: Item for this instance (collection-based only)<parallel.items>: Full collection being distributed (collection-based only)
// Inside a Function block within the parallel
const idx = <parallel.index>; // 0, 1, 2, ...
const item = <parallel.currentItem>; // This instance's itemThese references are only available for blocks inside the parallel container. They give you access to the current instance's context.
Outside the parallel (after it completes), reference the parallel block by its name to access aggregated results:
<ParallelBlockName.results>: Array of results from all instances
// If your parallel block is named "Process Tasks"
const allResults = <processtasks.results>;
// Returns: [result1, result2, result3, ...]After the parallel completes, use the parallel's block name (not parallel.) to access the collected results. The block name is normalized (lowercase, no spaces).
Example Use Cases
Batch API Processing - Process multiple API calls simultaneously
Parallel (Collection) → API (Call Endpoint) → Function (Aggregate)Multi-Model AI Processing - Get responses from multiple AI models concurrently
Parallel (["gpt-4o", "claude-3.7-sonnet", "gemini-2.5-pro"]) → Agent → Evaluator (Select Best)Advanced Features
Result Aggregation
Results from all parallel instances are automatically collected and accessible via the block name:
// In a Function block after a parallel named "Process Tasks"
const allResults = <processtasks.results>;
// Returns: [result1, result2, result3, ...]Instance Isolation
Each parallel instance runs independently:
- Separate variable scopes
- No shared state between instances
- Failures in one instance don't affect others
Limitations
Container blocks (Loops and Parallels) cannot be nested inside each other. This means:
- You cannot place a Loop block inside a Parallel block
- You cannot place another Parallel block inside a Parallel block
- You cannot place any container block inside another container block
While parallel execution is faster, be mindful of:
- API rate limits when making concurrent requests
- Memory usage with large datasets
- Maximum of 20 concurrent instances to prevent resource exhaustion
Parallel vs Loop
Understanding when to use each:
| Feature | Parallel | Loop |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | Concurrent | Sequential |
| Speed | Faster for independent operations | Slower but ordered |
| Order | No guaranteed order | Maintains order |
| Use case | Independent operations | Dependent operations |
| Resource usage | Higher | Lower |
Inputs and Outputs
Parallel Type: Choose between 'count' or 'collection'
Count: Number of instances to run (count-based)
Collection: Array or object to distribute (collection-based)
Available inside the parallel only:
<parallel.index>: Instance number (0-based)
<parallel.currentItem>: Item for this instance (collection-based only)
<parallel.items>: Full collection (collection-based only)
<blockname.results>: Array of all instance results (accessed via block name)
Access: Available in blocks after the parallel completes
Best Practices
- Independent operations only: Ensure operations don't depend on each other
- Handle rate limits: Add delays or throttling for API-heavy workflows
- Error handling: Each instance should handle its own errors gracefully