The Condition block branches workflow execution based on boolean expressions. Evaluate conditions using previous block outputs and route to different paths without requiring an LLM.
Configuration Options
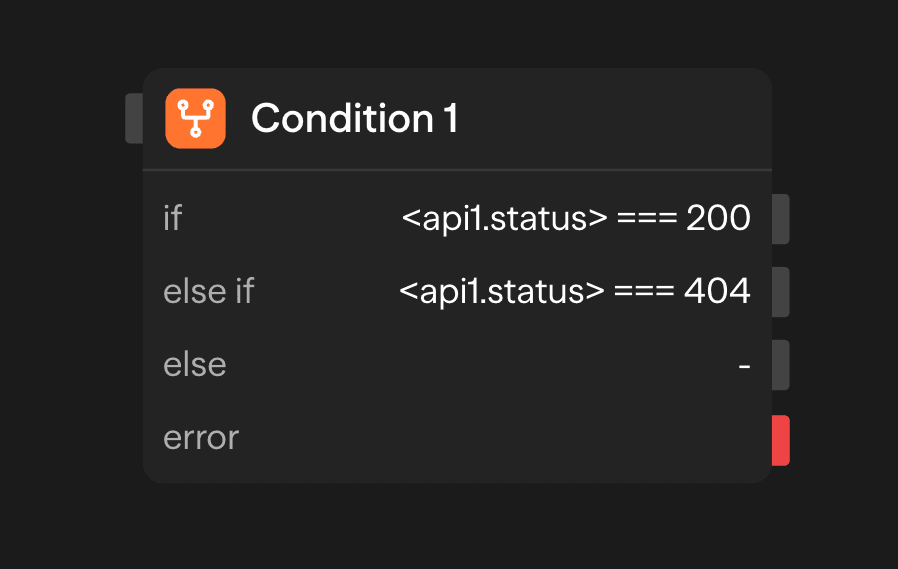
Conditions
Define one or more conditions that will be evaluated. Each condition includes:
- Expression: A JavaScript/TypeScript expression that evaluates to true or false
- Path: The destination block to route to if the condition is true
- Description: Optional explanation of what the condition checks
You can create multiple conditions that are evaluated in order, with the first matching condition determining the execution path.
Condition Expression Format
Conditions use JavaScript syntax and can reference input values from previous blocks.
// Check if a score is above a threshold
<agent.score> > 75// Check if a text contains specific keywords
<agent.text>.includes('urgent') || <agent.text>.includes('emergency')// Check multiple conditions
<agent.age> >= 18 && <agent.country> === 'US'Accessing Results
After a condition evaluates, you can access its outputs:
<condition.result>: Boolean result of the condition evaluation<condition.matched_condition>: ID of the condition that was matched<condition.content>: Description of the evaluation result<condition.path>: Details of the chosen routing destination
Advanced Features
Complex Expressions
Use JavaScript operators and functions in conditions:
// String operations
<user.email>.endsWith('@company.com')
// Array operations
<api.tags>.includes('urgent')
// Mathematical operations
<agent.confidence> * 100 > 85
// Date comparisons
new Date(<api.created_at>) > new Date('2024-01-01')Multiple Condition Evaluation
Conditions are evaluated in order until one matches:
// Condition 1: Check for high priority
<ticket.priority> === 'high'
// Condition 2: Check for urgent keywords
<ticket.subject>.toLowerCase().includes('urgent')
// Condition 3: Default fallback
trueError Handling
Conditions automatically handle:
- Undefined or null values with safe evaluation
- Type mismatches with appropriate fallbacks
- Invalid expressions with error logging
- Missing variables with default values
Outputs
<condition.result>: Boolean result of the evaluation<condition.matched_condition>: ID of the matched condition<condition.content>: Description of the evaluation result<condition.path>: Details of the chosen routing destination
Example Use Cases
Customer Support Routing - Route tickets based on priority
API (Ticket) → Condition (priority === 'high') → Agent (Escalation) or Agent (Standard)Content Moderation - Filter content based on analysis
Agent (Analyze) → Condition (toxicity > 0.7) → Moderation or PublishUser Onboarding Flow - Personalize onboarding based on user type
Function (Process) → Condition (account_type === 'enterprise') → Advanced or SimpleBest Practices
- Order conditions correctly: Place more specific conditions before general ones to ensure specific logic takes precedence over fallbacks
- Use the else branch when needed: If no conditions match and the else branch is not connected, the workflow branch will end gracefully. Connect the else branch if you need a fallback path for unmatched cases
- Keep expressions simple: Use clear, straightforward boolean expressions for better readability and easier debugging
- Document your conditions: Add descriptions to explain the purpose of each condition for better team collaboration and maintenance
- Test edge cases: Verify conditions handle boundary values correctly by testing with values at the edges of your condition ranges