The API block connects your workflow to external services through HTTP requests. Supports GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and PATCH methods for interacting with REST APIs.
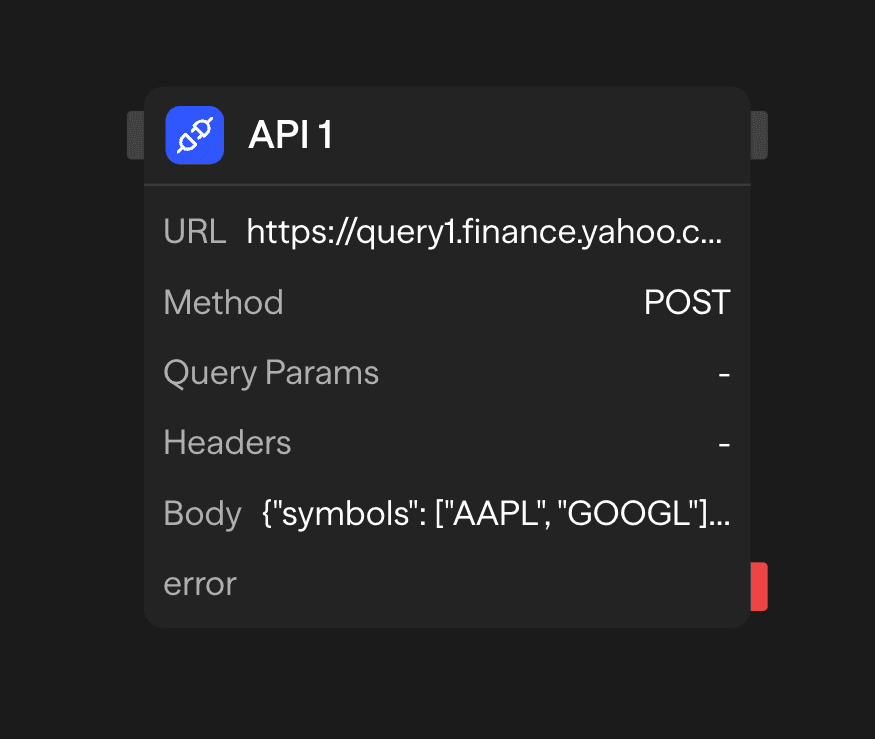
Configuration Options
URL
The endpoint URL for the API request. This can be:
- A static URL entered directly in the block
- A dynamic URL connected from another block's output
- A URL with path parameters
Method
Select the HTTP method for your request:
- GET: Retrieve data from the server
- POST: Send data to the server to create a resource
- PUT: Update an existing resource on the server
- DELETE: Remove a resource from the server
- PATCH: Partially update an existing resource
Query Parameters
Define key-value pairs that will be appended to the URL as query parameters. For example:
Key: apiKey
Value: your_api_key_here
Key: limit
Value: 10These would be added to the URL as ?apiKey=your_api_key_here&limit=10.
Headers
Configure HTTP headers for your request. Common headers include:
Key: Content-Type
Value: application/json
Key: Authorization
Value: Bearer your_token_hereRequest Body
For methods that support a request body (POST, PUT, PATCH), you can define the data to send. The body can be:
- JSON data entered directly in the block
- Data connected from another block's output
- Dynamically generated during workflow execution
Accessing Results
After an API request completes, you can access its outputs:
<api.data>: The response body data from the API<api.status>: HTTP status code (200, 404, 500, etc.)<api.headers>: Response headers from the server<api.error>: Error details if the request failed
Advanced Features
Dynamic URL Construction
Build URLs dynamically using variables from previous blocks:
// In a Function block before the API
const userId = <start.userId>;
const apiUrl = `https://api.example.com/users/${userId}/profile`;Request Retries
The API block automatically handles:
- Network timeouts with exponential backoff
- Rate limit responses (429 status codes)
- Server errors (5xx status codes) with retry logic
- Connection failures with reconnection attempts
Response Validation
Validate API responses before processing:
// In a Function block after the API
if (<api.status> === 200) {
const data = <api.data>;
// Process successful response
} else {
// Handle error response
console.error(`API Error: ${<api.status>}`);
}Outputs
<api.data>: Response body data from the API<api.status>: HTTP status code<api.headers>: Response headers<api.error>: Error details if request failed
Example Use Cases
Fetch User Profile Data - Retrieve user information from external service
Function (Build ID) → API (GET /users/{id}) → Function (Format) → ResponsePayment Processing - Process payment through Stripe API
Function (Validate) → API (Stripe) → Condition (Success) → Supabase (Update)Best Practices
- Use environment variables for sensitive data: Don't hardcode API keys or credentials
- Handle errors gracefully: Connect error handling logic for failed requests
- Validate responses: Check status codes and response formats before processing data
- Respect rate limits: Be mindful of API rate limits and implement appropriate throttling