The Response block formats and sends structured HTTP responses back to API callers. Use it to return workflow results with proper status codes and headers.
Response blocks are terminal blocks - they end workflow execution and cannot connect to other blocks.
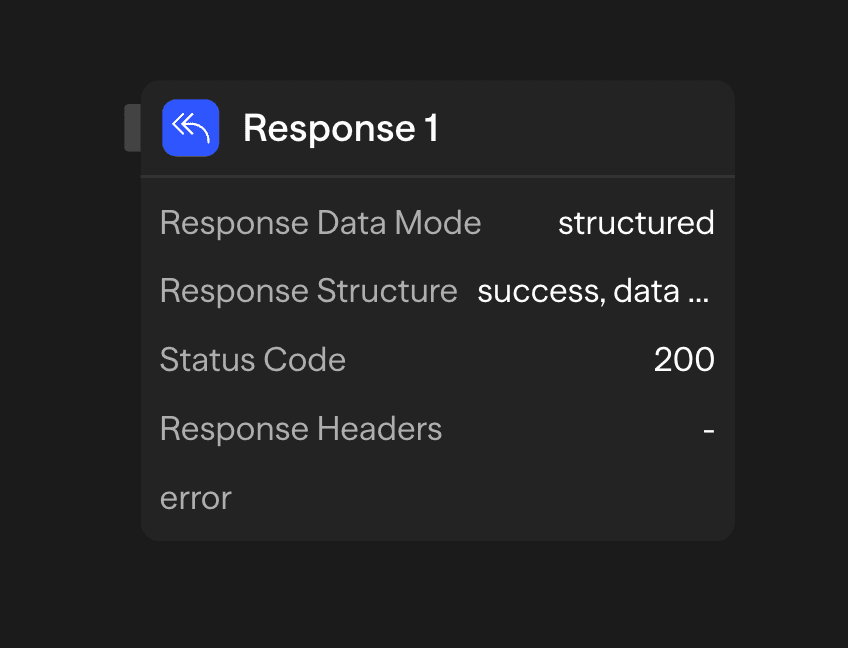
Configuration Options
Response Data
The response data is the main content that will be sent back to the API caller. This should be formatted as JSON and can include:
- Static values
- Dynamic references to workflow variables using the
<variable.name>syntax - Nested objects and arrays
- Any valid JSON structure
Status Code
Set the HTTP status code for the response (defaults to 200):
Success (2xx):
- 200: OK - Standard success response
- 201: Created - Resource successfully created
- 204: No Content - Success with no response body
Client Error (4xx):
- 400: Bad Request - Invalid request parameters
- 401: Unauthorized - Authentication required
- 404: Not Found - Resource doesn't exist
- 422: Unprocessable Entity - Validation errors
Server Error (5xx):
- 500: Internal Server Error - Server-side error
- 502: Bad Gateway - External service error
- 503: Service Unavailable - Service temporarily down
Response Headers
Configure additional HTTP headers to include in the response.
Headers are configured as key-value pairs:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | application/json |
| Cache-Control | no-cache |
| X-API-Version | 1.0 |
Example Use Cases
API Endpoint Response - Return structured data from a search API
Agent (Search) → Function (Format & Paginate) → Response (200, JSON)Webhook Confirmation - Acknowledge webhook receipt and processing
Webhook Trigger → Function (Process) → Response (200, Confirmation)Error Response Handling - Return appropriate error responses
Condition (Error Detected) → Router → Response (400/500, Error Details)Outputs
Response blocks are terminal - they end workflow execution and send the HTTP response to the API caller. No outputs are available to downstream blocks.
Variable References
Use the <variable.name> syntax to dynamically insert workflow variables into your response:
{
"user": {
"id": "<variable.userId>",
"name": "<variable.userName>",
"email": "<variable.userEmail>"
},
"query": "<variable.searchQuery>",
"results": "<variable.searchResults>",
"totalFound": "<variable.resultCount>",
"processingTime": "<variable.executionTime>ms"
}Variable names are case-sensitive and must match exactly with the variables available in your workflow.
Best Practices
- Use meaningful status codes: Choose appropriate HTTP status codes that accurately reflect the outcome of the workflow
- Structure your responses consistently: Maintain a consistent JSON structure across all your API endpoints for better developer experience
- Include relevant metadata: Add timestamps and version information to help with debugging and monitoring
- Handle errors gracefully: Use conditional logic in your workflow to set appropriate error responses with descriptive messages
- Validate variable references: Ensure all referenced variables exist and contain the expected data types before the Response block executes