The Loop block is a container that executes blocks repeatedly. Iterate over collections, repeat operations a fixed number of times, or continue while a condition is met.
Loop blocks are container nodes that hold other blocks inside them. The contained blocks execute multiple times based on your configuration.
Configuration Options
Loop Type
Choose between four types of loops:
For Loop (Iterations) - A numeric loop that executes a fixed number of times:
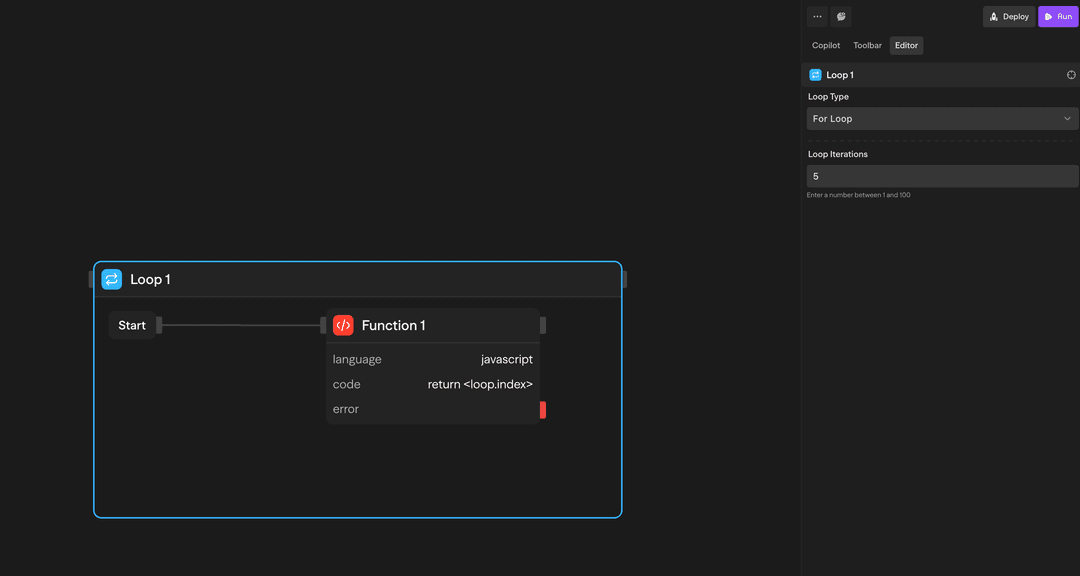
Use this when you need to repeat an operation a specific number of times.
Example: Run 5 times
- Iteration 1
- Iteration 2
- Iteration 3
- Iteration 4
- Iteration 5ForEach Loop (Collection) - A collection-based loop that iterates over each item in an array or object:
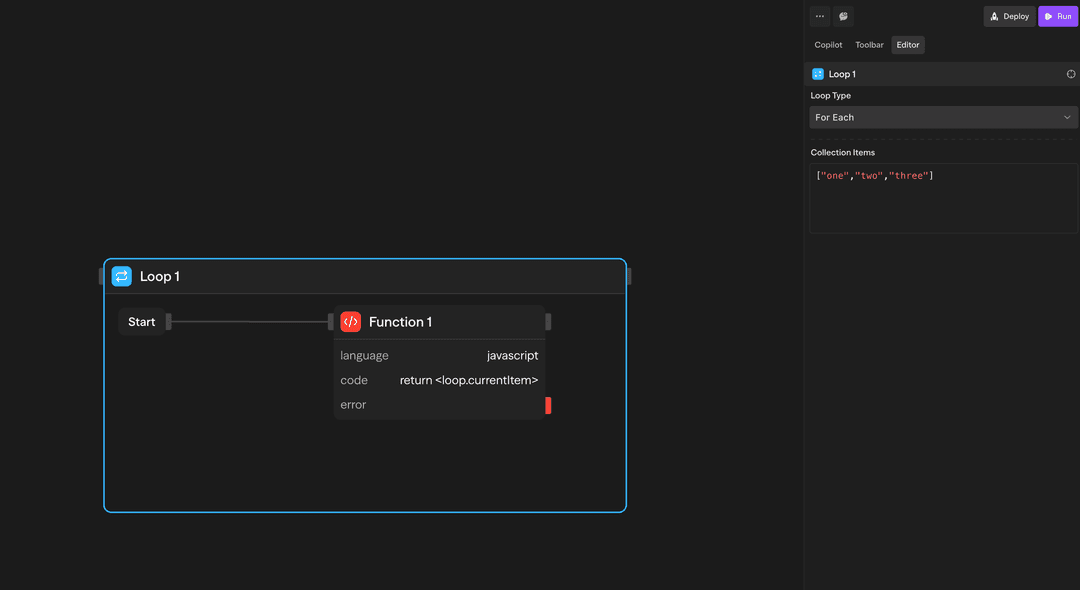
Use this when you need to process a collection of items.
Example: Process ["apple", "banana", "orange"]
- Iteration 1: Process "apple"
- Iteration 2: Process "banana"
- Iteration 3: Process "orange"While Loop (Condition-based) - Continues executing while a condition evaluates to true:
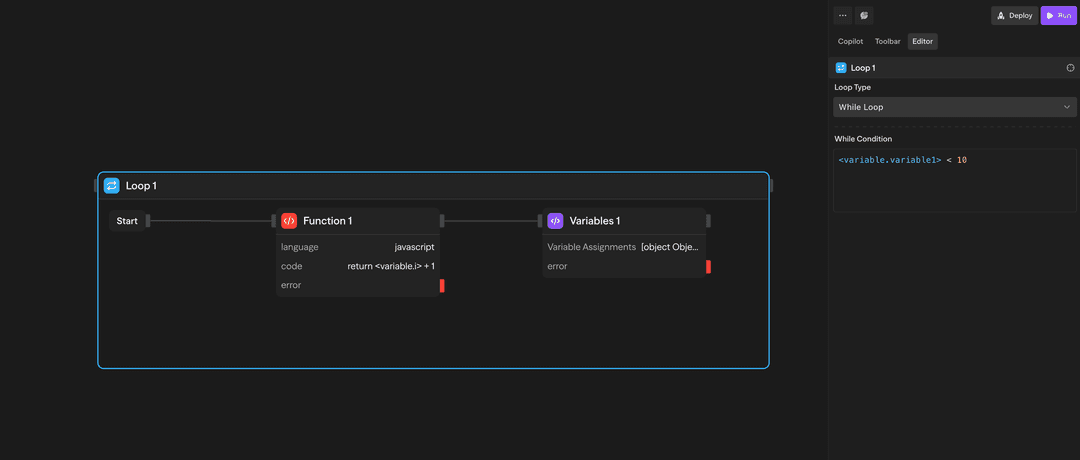
Use this when you need to loop until a specific condition is met. The condition is checked before each iteration.
Example: While {"<variable.i>"} < 10
- Check condition → Execute if true
- Inside loop: Increment {"<variable.i>"}
- Inside loop: Variables assigns i = {"<variable.i>"} + 1
- Check condition → Execute if true
- Check condition → Exit if falseDo-While Loop (Condition-based) - Executes at least once, then continues while a condition is true:
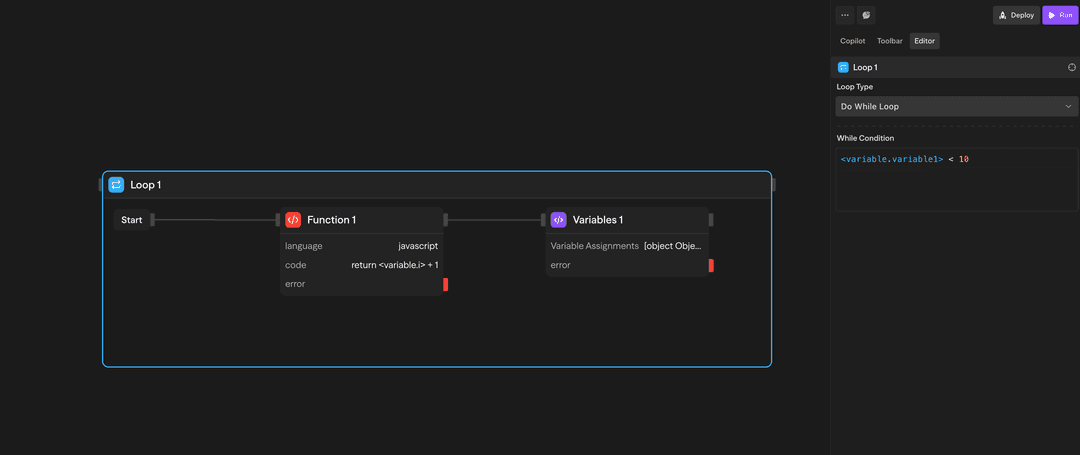
Use this when you need to execute at least once, then loop until a condition is met. The condition is checked after each iteration.
Example: Do-while {"<variable.i>"} < 10
- Execute blocks
- Inside loop: Increment {"<variable.i>"}
- Inside loop: Variables assigns i = {"<variable.i>"} + 1
- Check condition → Continue if true
- Check condition → Exit if falseHow to Use Loops
Creating a Loop
- Drag a Loop block from the toolbar onto your canvas
- Configure the loop type and parameters
- Drag other blocks inside the loop container
- Connect the blocks as needed
Referencing Loop Data
There's an important distinction between referencing loop data from inside vs outside the loop:
Inside the loop, use <loop.> references to access the current iteration context:
<loop.index>: Current iteration number (0-based)<loop.currentItem>: Current item being processed (forEach only)<loop.items>: Full collection being iterated (forEach only)
// Inside a Function block within the loop
const idx = <loop.index>; // 0, 1, 2, ...
const item = <loop.currentItem>; // Current itemThese references are only available for blocks inside the loop container. They give you access to the current iteration's context.
Outside the loop (after it completes), reference the loop block by its name to access aggregated results:
<LoopBlockName.results>: Array of results from all iterations
// If your loop block is named "Process Items"
const allResults = <processitems.results>;
// Returns: [result1, result2, result3, ...]After the loop completes, use the loop's block name (not loop.) to access the collected results. The block name is normalized (lowercase, no spaces).
Example Use Cases
Processing API Results - ForEach loop processes customer records from an API
API (Fetch) → Loop (ForEach) → Agent (Analyze) → Function (Store)Iterative Content Generation - For loop generates multiple content variations
Loop (5x) → Agent (Generate) → Evaluator (Score) → Function (Select Best)Counter with While Loop - While loop processes items with counter
Variables (i=0) → Loop (While i<10) → Agent (Process) → Variables (i++)Advanced Features
Limitations
Container blocks (Loops and Parallels) cannot be nested inside each other. This means:
- You cannot place a Loop block inside another Loop block
- You cannot place a Parallel block inside a Loop block
- You cannot place any container block inside another container block
If you need multi-dimensional iteration, consider restructuring your workflow to use sequential loops or process data in stages.
Loops execute sequentially, not in parallel. If you need concurrent execution, use the Parallel block instead.
Inputs and Outputs
Loop Type: Choose between 'for', 'forEach', 'while', or 'doWhile'
Iterations: Number of times to execute (for loops)
Collection: Array or object to iterate over (forEach loops)
Condition: Boolean expression to evaluate (while/do-while loops)
Available inside the loop only:
<loop.index>: Current iteration number (0-based)
<loop.currentItem>: Current item being processed (forEach only)
<loop.items>: Full collection (forEach only)
<blockname.results>: Array of all iteration results (accessed via block name)
Structure: Results maintain iteration order
Access: Available in blocks after the loop completes
Best Practices
- Set reasonable limits: Keep iteration counts reasonable to avoid long execution times
- Use ForEach for collections: When processing arrays or objects, use ForEach instead of For loops
- Handle errors gracefully: Consider adding error handling inside loops for robust workflows