What It Does
Drop a Workflow block when you want to call a child workflow as part of a larger flow. The block runs the latest deployed version of that workflow, waits for it to finish, and then continues with the parent.
Configure It
- Pick a workflow from the dropdown (self-references are blocked to prevent loops).
- Map inputs: If the child workflow has an Input Form trigger, you'll see each field and can connect parent variables. The mapped values are what the child receives.
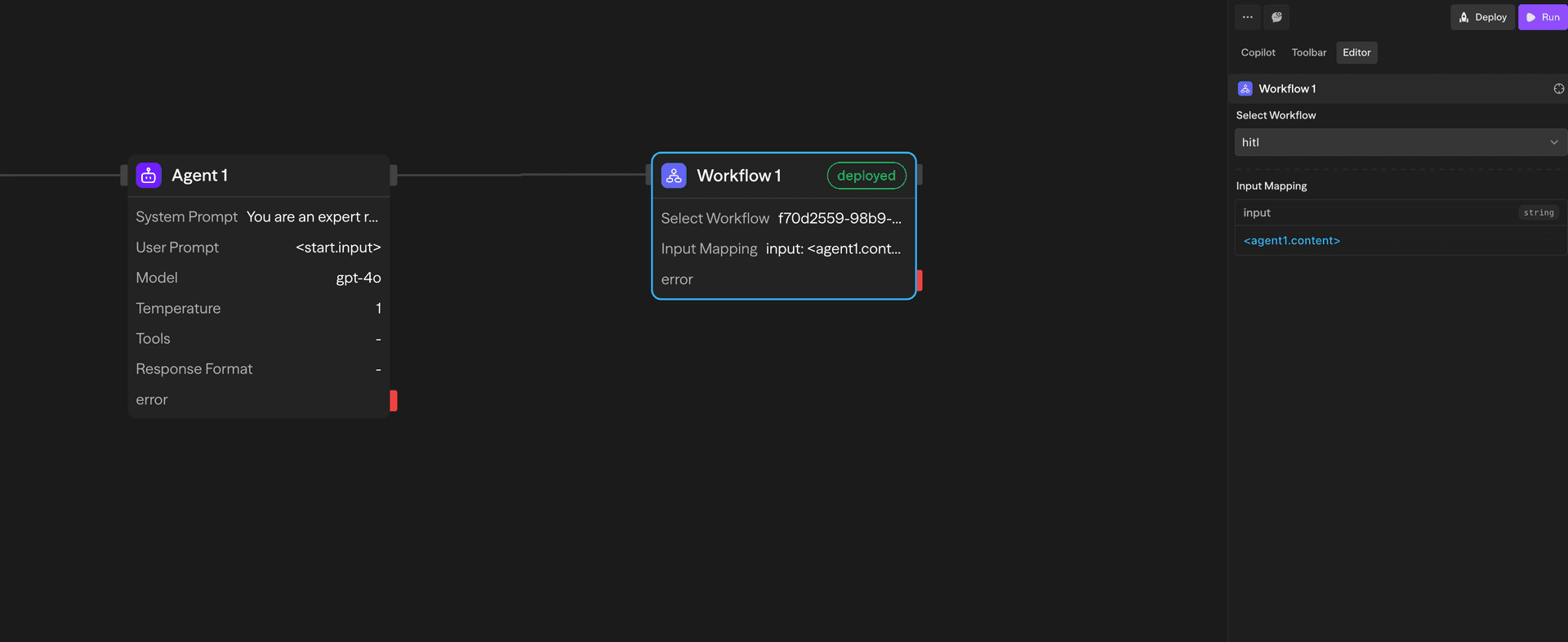
- Outputs: After the child finishes, the block exposes:
result– the child workflow's final responsesuccess– whether it ran without errorserror– message when the run fails
Deployment Status Badge
The Workflow block displays a deployment status badge to help you track whether the child workflow is ready to execute:
- Deployed – The child workflow has been deployed and is ready to use. The block will execute the current deployed version.
- Undeployed – The child workflow has never been deployed. You must deploy it before the Workflow block can execute it.
- Redeploy – Changes have been detected in the child workflow since the last deployment. Click the badge to redeploy the child workflow with the latest changes.
The Workflow block always executes the most recent deployed version of the child workflow, not the editor version. Make sure to redeploy after making changes to ensure the block uses the latest logic.
Execution Notes
- Child workflows run in the same workspace context, so environment variables and tools carry over.
- The block uses deployment versioning: any API, schedule, webhook, manual, or chat execution calls the deployed snapshot. Redeploy the child when you change it.
- If the child fails, the block raises an error unless you handle it downstream.
Keep child workflows focused. Small, reusable flows make it easier to combine them without creating deep nesting.